So far, most studies linking periodontal disease to systemic diseases have focused on diabetes, cardiovascular disease and adverse pregnancy outcomes. However, there are other systemic diseases and


So far, most studies linking periodontal disease to systemic diseases have focused on diabetes, cardiovascular disease and adverse pregnancy outcomes. However, there are other systemic diseases and
During pregnancy, due to hormonal changes, there is a certain systemic propensity to periodontal problems. The most pathogenic bacteria of the biofilm, (Socransky’s orange and

Periodontitis and diabetes are chronic diseases of ever-growing worldwide prevalence. Ninety percent of the population is estimated to have some type of oral infectious disease, including

The relationship between periodontal disease and cardiovascular disease has been extensively studied over the past decades through in vitro studies, animal models, case-control studies, cohort studies, randomized
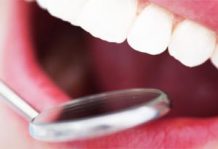
Gingivitis and periodontitis are two stages of periodontal disease, which are generally chronic, infectious and inflammatory in nature, are located in the tooth support tissues and which

Peri-implant mucositis has a low potential for inflammatory response, and thus, when oral biofilm accumulation exists, the inflammation spreads deeper, possibly causing implant loss. Peri-implantitis has an

Because peri-implant tissues have a lower capacity to react to the accumulation of oral biofilm compared to periodontal tissues, peri-implant disease is highly prevalent among implant patients.
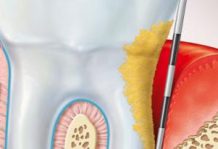
Periodontitis is the most advanced form of gum disease and can potentially have an impact on a systemic level, with a prevalence of 35.4% in adults between
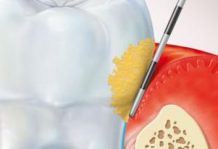
Among the different forms of gum disease, gingivitis is the most common to occur in humans, with a prevalence of 59.8% in adults between the ages of

The data reflects the importance of biofilms as a source for local infections that can trigger complications on a systemic level.
Many non-pathogenic organisms exist that produce