Peri-implant mucositis has a low potential for inflammatory response, and thus, when oral biofilm accumulation exists, the inflammation spreads deeper, possibly causing implant loss. Peri-implantitis has an


Peri-implant mucositis has a low potential for inflammatory response, and thus, when oral biofilm accumulation exists, the inflammation spreads deeper, possibly causing implant loss. Peri-implantitis has an

Because peri-implant tissues have a lower capacity to react to the accumulation of oral biofilm compared to periodontal tissues, peri-implant disease is highly prevalent among implant patients.
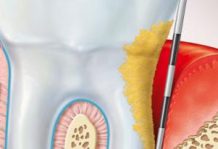
Periodontitis is the most advanced form of gum disease and can potentially have an impact on a systemic level, with a prevalence of 35.4% in adults between
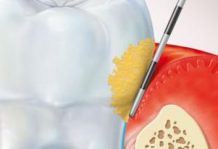
Among the different forms of gum disease, gingivitis is the most common to occur in humans, with a prevalence of 59.8% in adults between the ages of

The data reflects the importance of biofilms as a source for local infections that can trigger complications on a systemic level.
Many non-pathogenic organisms exist that produce
Factors that regulate the composition, development, amount, coexistence and distribution of oral microorganisms on surfaces of the oral cavity (primary ecosystems) are known as environmental determinants. There

The primary colonisers are mainly gram-positive bacteria – cocci and bacilli – which bind to salivary protein antigens, by specificity of
In oligotrophic environments (lack of nutrients), most bacteria (and some fungi) leave their state of individual planktonic cells to grow as biofilms, forming colonies embedded in a

This case is a clear example of the importance of regular follow-up and maintenance in patients who undergo implant treatment, particularly in high risk patients, like the

Oral biofilm has pathogenic potential and its presence is associated with the development of caries, gingivitis, periodontal disease, peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis.
The process of oral biofilm